Firewall Manager access (IT MSP)
ProtectAn yourIT existingmanaged Fortigateservices orprovider Palomaintained investmentsmultiple Fortinet firewalls on behalf of customers, often responding to urgent service desk requests requiring 24/7 access. These firewalls were deployed across various locations and managed by multiple members of the network team.
Due to security concerns, access to manage these firewalls was restricted to several office/static IP addresses deemed trustworthy. However, remote access remained necessary, including for select customers who self-managed their firewall/rules. To facilitate remote firewall management, a VPN was exposed to the Internet. This approach introduced unnecessary attack surface and another Internet-exposed asset/entry point. It also presented challenges related to authorization as the VPN was shared with MSP staff and select customers.
Objective:
Enable remote firewall management from directtrusted internetIP exposureaddresses byon introducingthe Knocknoc.Internet, linked to an authorized Entra group login, eliminating the need for an Internet-exposed VPN nor requiring on-premise network access.
RemoteOutcome:
Firewall management andusers administrationseamlessly interfaces,logged VPNin services/ports or any service offered can be protected, requiring a centralised login prior to presenting network exposure. A quick way to support remote management withoutusing the InternetEntra exposureexternal risk,client removesconnector. the threat of zero-days as it is simply invisible prior to logging in to Knocknoc, which opens access just in time.
This cansolution beaccommodated achievedboth inMSP multiplestaff waysand throughexternal activecustomers, orallowing passive firewall orchestration , effectively adding network application whitelisting only after a successful authorized usersecure login to the networkappropriate edge.firewall for management tasks. All access was logged, and multi-factor authentication was implemented without adding complexity or making significant changes to the existing Fortinet configurations.
Technical how:
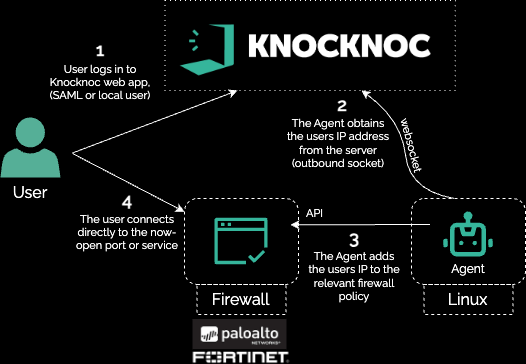
In this example half the Fortinet firewalls were 'actively' managed by Knocknoc, with the other half 'passively' orchestrated. This allowed authorized firewall managers to securely manage the firewall devices when required, but presented zero attack surface to the broader Internet, and did not require a VPN whatsoever allowing that device to be deprecated.
Shown below is the direct-Active orchestration model, where Knocknoc adds the trusted/authenticated IP address to the relevant policy on the Fortinet, exposing the VPN services to an IP address only after they have successfully authenticated.model:
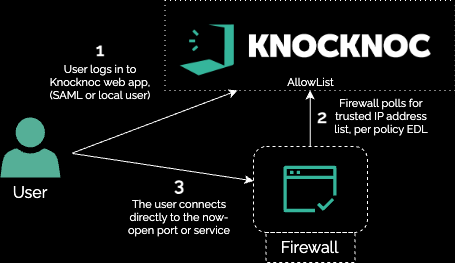
AlternativelyThe another agentlessdevices deployment can be established usingutilized the AllowListPassive feature:mode:
This can be combined in a passive-allowlist model along with an API call which updates the policies (causing a live poll), giving you the best of both worlds - low privilege API access along with a polled allowlist.
This can be used to remove the attack surface of VPN services/protocols prior to centralized login or prevent asset exposure to zero-day attacks as they simply inaccessible.
If you need to urgently reduce direct exposure of your Fortigate, Palo or other appliances, please talk to us.